In the realm of emerging technologies, one of the common confusions many learners battle with is understanding the distinction between artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). It’s a common concern, especially among those contemplating taking up a career in either field. In this article, we’ll help you gain a better understanding of the nuances, so you can make the right choice for you.
Defining AI and ML
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence, commonly known as AI, encompasses the concept of machines being programmed to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks range from problem-solving and learning to planning and natural language understanding. With AI, the objective is to create systems that can perform independently and adapt over time.
What is Machine Learning?
On the other hand, m is a subset of AI that’s focused on enabling machines to learn from data to provide solutions to problems or make decisions. Instead of relying on hardcoded algorithms, ML models adapt based on the data they process, enhancing their performance over time.
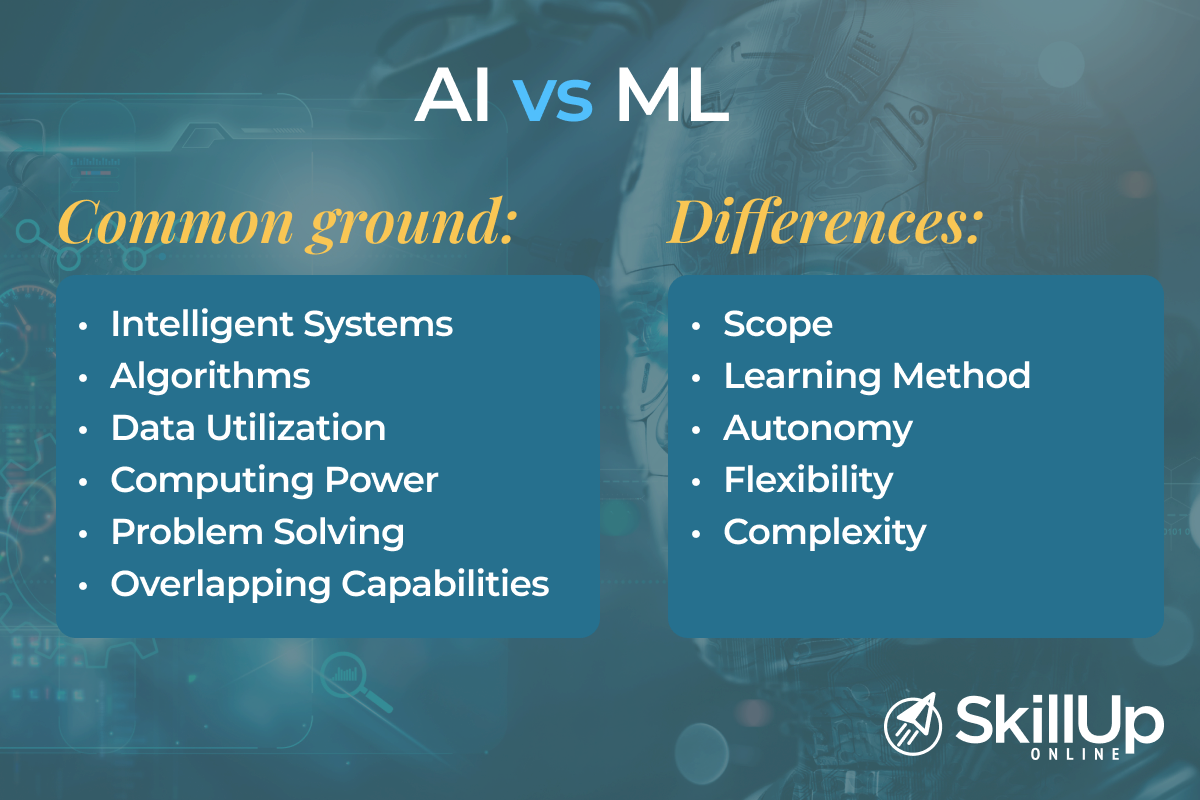
The relationship between these two is complex, akin to two overlapping circles in a Venn diagram. So, to shed light on this relationship, let’s delve into where they overlap and differ.
The Overlap and the Differences
Common Ground
- Intelligent Systems: Both AI and ML share the overarching goal of creating intelligent systems. They aim to develop algorithms and models that can make decisions and perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
- Algorithms: AI and ML rely on algorithms as the building blocks of their systems. These algorithms process data and make predictions or decisions based on patterns and information.
- Data Utilization: Both fields heavily depend on data. They use data to train models, make predictions, and optimize performance.
- Computing Power: AI and ML often require substantial computing power, especially for training complex models.
- Problem Solving: AI and ML are problem-solving tools. They can be applied to a wide range of tasks, from natural language processing to image recognition, with the aim of automating or enhancing human-like decision-making.
- Overlapping Capabilities: There is an overlap in capabilities between AI and ML. For instance, both can excel in natural language processing (NLP), sentiment analysis, recommendation systems, and predictive analytics.
Differences
- Scope
- AI has a broader scope encompassing all aspects of creating intelligent agents, including reasoning, perception, problem solving, and decision-making.
- ML is a subset of AI, focusing specifically on developing algorithms that can learn from data and improve their performance over time.
- Learning Method
- AI includes various approaches beyond ML, such as rule-based systems, expert systems, and symbolic reasoning.
- ML primarily relies on data-driven approaches, where models learn patterns and make predictions based on training data.
- Autonomy
- AI systems aim to exhibit autonomous behavior, for example making decisions and taking actions independently.
- ML models, while capable of learning from data, typically require predefined features and guidance for their training.
- Flexibility
- AI systems are designed to handle a wide range of tasks and adapt.
- ML models are often tailored to specific tasks or domains, and retraining may be required for new tasks.
- Complexity
- AI systems can be highly complex and may involve symbolic reasoning, knowledge representation, and planning.
- ML models can be simpler in structure, focusing on statistical patterns in data.
If you’re keen to get a good grounding in both AI and ML, SkillUp Online’s TechMaster Certificate Program in AI with Data Science offers a broad curriculum covering both subjects extensively.
Decoding AI Course Content
AI courses cover an expansive set of topics. Good examples include:
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This domain focuses on enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Robotics: A branch that integrates engineering and AI to create robots that can perform tasks in real-world settings.
- Computer Vision: This sub-field trains machines to interpret and make decisions based on visual data.
- Expert Systems: These AI programs mimic a human expert’s decision-making abilities in a particular field.
- Ethical AI: Ethical considerations around data usage, algorithmic bias, and societal impact are also crucial topics.
Key Skills Developed
When you embark on an AI course, the skills you acquire are multi-dimensional and include:
- Algorithmic Thinking: Understanding the logic and sequences that drive AI.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing and interpreting complex data sets to make decisions.
- Programming Skills: Proficiency in languages like Python is often essential.
- Ethical Judgement: Evaluating the ethical implications of AI implementations.
- Soft Skills: Skills like problem-solving and critical thinking are invaluable in AI.
Course Length and Complexity
The duration and intricacy of AI courses can vary widely:
- Short Courses: offers courses like “AI for Everyone: Master the Basics” that may last a few weeks but offer foundational knowledge.
- Mid-Length Programs: Courses like the “Applied AI IBM Professional Certificate” span a few months and delve deeper into specialized topics.
- Long-Term Programs: For those looking for an exhaustive understanding, longer programs such as TechMaster Certificate Program in AI with Data Science can last up to 11 months.
Understanding these nuances helps you pick a program that matches your interests and fits your schedule and learning pace.
Decoding ML Course Content
Machine learning courses have their own set of unique focus areas, some of which are:
- Supervised Learning: Teaching machines to make predictions based on labeled data.
- Unsupervised Learning: Algorithms learn from data without human intervention.
- Reinforcement Learning: Machines learn optimal actions through trial and error.
- Ensemble Learning: Multiple models are used to improve overall performance.
- Time Series Analysis: This is crucial for forecasting and trend analysis in various industries.
Key Skills Developed
Machine learning courses equip you with a particular set of competencies, such as:
- Statistical Analysis: The ability to interpret data and infer patterns.
- Model Evaluation: Understanding how to judge the effectiveness of a machine learning model.
- Data Preprocessing: Skills in preparing data for efficient machine learning.
- Algorithm Customization: Adapting existing algorithms for specialized requirements.
- Problem-Solving: Tackling real-world challenges with machine learning solutions.
Course Length and Complexity
The duration and complexity of ML courses also cover short, mid-length, and long-term programs.
- Short Courses: Courses like “Foundation of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning”are perfect for those in a hurry.
- Medium Term: Platform specific options like “AI-102 Designing and Implementing a Microsoft Azure AI Solution”offer more in-depth study and takes a few months and give you skills specific to a platform, in the instance Microsoft Azure.
- Long-Term Programs: For a comprehensive understanding, you might prefer longer commitments like the TechMaster Certificate Program in AI with Data Science.
By understanding what each ML course offers regarding topics, skills, and length, you’re better equipped to make an informed decision that aligns with your career and learning goals.
Why Choose an ML Course
Career Opportunities
Opting for an ML course can open up career paths such as data scientist, ML engineer, and natural language processing expert. According to the Turing , machine learning career opportunities will increase by 200% in the coming decade.
Academic Relevance
Machine learning also offers substantial academic prospects. Many educational institutes and organizations offer ML research positions, internships, and scholarships. ML courses often serve as a stepping stone to more specialized academic research in neural networks or quantum computing.
Industry Applications
Machine learning has distinct applications in multiple sectors:
- Finance: Fraud detection and algorithmic trading are popular ML applications.
- Healthcare: Predictive analytics for patient outcomes is another crucial area.
- Energy: ML algorithms help in optimizing energy consumption.
Choosing an ML course could be your ticket to an exciting, lucrative, and impactful career in various industries.
Why Choose an AI Course
Choosing an AI course can significantly broaden your career horizons. From AI engineering to data analysis, the demand for AI expertise is ever-growing. As per LinkedIn data as of December 2023, there are over 64,000 job openings in AI in the US. Not only do these roles offer attractive salaries, but they also allow for meaningful work in various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and finance.
Academic Relevance
Artificial Intelligence is not just about job opportunities; it’s also an academic field with considerable research prospects. AI courses can provide a foundation for postgraduate studies or even a Ph.D. For example, many courses include research papers and offer networking opportunities with industry experts.
Industry Applications
The power of AI extends to various industries:
- Healthcare: AI assists in drug discovery and patient diagnostics.
- Retail: AI algorithms help in customer targeting and inventory management.
- Manufacturing: Automating tasks and predictive maintenance are popular applications.
Selecting the Right Course
Your Learning Objectives
Before diving into any course, setting clear learning objectives is essential. Are you looking to become proficient in a specific technology or looking for a broad understanding of AI and ML concepts? Knowing your goals will help you choose the right course.
For example, if you are aiming to develop hands-on experience with AI implementations, you might find SkillUp Online’s Applied AI IBM Professional Certificate to be an excellent match for your needs. Another possible course to explore is the Google Machine Learning Crash Course with Tensor Flow API
Industry Requirements
Industry demands are a crucial consideration. As AI and ML technologies evolve, the skills valued by employers are constantly changing. For instance, you may need specialized AI capabilities for diagnosis and treatment planning in the healthcare industry.
Personal Interest
the power of passion in career success. When you’re genuinely passionate about a subject within AI or ML, you’re more likely to be intrinsically motivated to learn and excel in that area. This internal motivation can drive you to go above and beyond in your studies, projects, and work.
Passion also fosters creativity. When you are passionate about a specific aspect of AI or ML, you are more inclined to approach problems creatively, think outside the box, and come up with innovative solutions.
Moreover, AI and ML are vast fields with numerous subdomains. Your interests can guide you toward a specialization that aligns with your passion. Whether it’s computer vision, natural language processing, robotics or ethical AI, specializing in an area you love can lead to a more fulfilling career.
Complementary Skills
Data Science and AI/ML
While AI and ML provide the engine for intelligent solutions, data science offers the fuel. Understanding how to gather, clean, and interpret data is crucial for any AI/ML project. Moreover, a firm grasp of statistical methods can help you make more accurate predictions and decisions.
Ethical Considerations in AI/ML
As AI and ML technologies become more integrated into society, ethical considerations like bias, transparency, and data privacy have become increasingly important. Awareness of these ethical dimensions can set you apart as a responsible AI/ML professional.
Your Path Forward in AI and ML
Deciding Between AI and ML Courses
By now, you should have a clearer idea of the distinct realms of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Whether you’re fascinated by the broad possibilities of AI or the focused, data-driven nature of ML, the choice ultimately depends on your interests, career goals, and the challenges you want to solve.
If you’re still on the fence, our blogs How to Start Your AI Career & Should I Choose a Career in AI or Data Science? can give you more perspectives to make an informed decision.
 If you would like to know more about how you can build skills and get started, contact our Learner Support Team at [email protected]. They will be more than happy to guide you on your next steps.
If you would like to know more about how you can build skills and get started, contact our Learner Support Team at [email protected]. They will be more than happy to guide you on your next steps.
SkillUp Online